DRG / DRB express train carriage
When the fourth class of cars was abolished at the Deutsche Reichsbahn Gesellschaft (DRG) in 1928, it was the impetus for the development of a new type of car: the DRG express train car. These cars were the replacement of the compartment cars with a large number of doors for quicker entry and exit. To ensure that entry and exit could continue to happen quickly, these carriages had double doors in what was then the third class area. The cars were designed as through cars. In terms of appearance, they were adapted to the express train cars of the time. The basic characteristics of the cars were implemented in all types of DRG express train cars.
Riveted Wagons of the interchangeable Design
Welded test cars and first welded series cars
The first welded test cars were built in 1932. The Type 33 baggage wagons were welded, but had the same dimensions as the Type 32. From 1934 onwards, the first 42 series C4i-34 wagons were delivered as welded wagons. Their spatial arrangement corresponded to the riveted cars of the C4i-30 model. From 1935 onwards, improved, welded express train cars were built in series, the basic features of which corresponded to their predecessors.
Welded Wagons
From the C4i-35 model onwards, the windows have been enlarged (the bottom edge of the window is 150mm deeper and widened by 200mm. The seat spacing has also been increased. These two use groups had Görlitz III light bogies. The cars are ventilated by Wendler fans (individual cars that were built after the war based on these cars also had cuckoo-type roof fans). Originally these cars had open scissor gates at the crossings, which were then replaced by folding bellows on the DB.


The exception were the express train cars of the Karwendel Express with bellows.
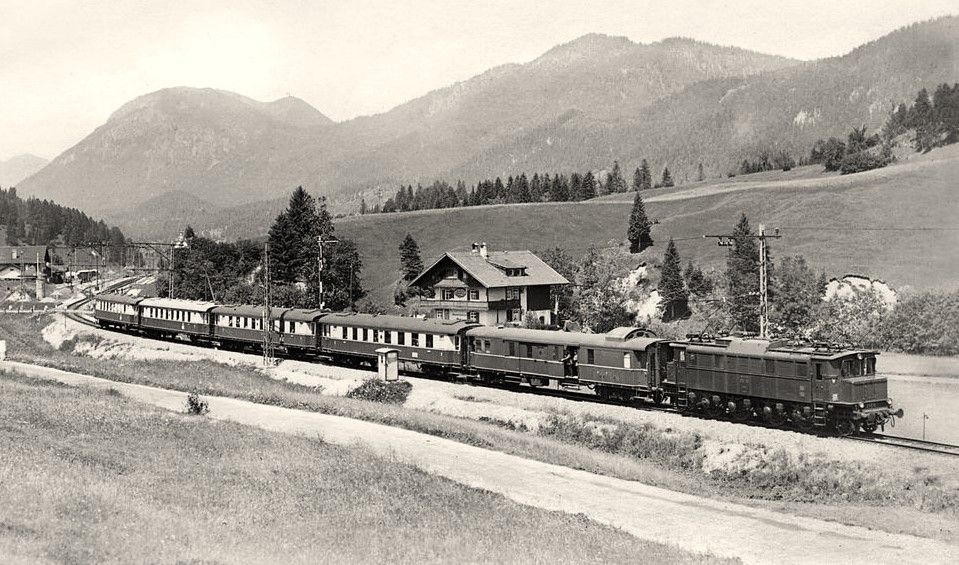

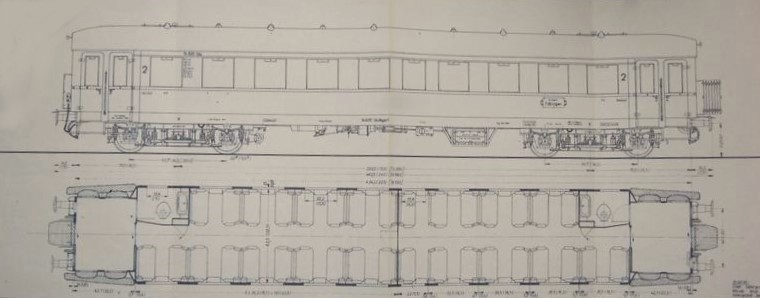
DRG / DRB express train carriage with open scissor gate transition.
a.s.modellbahn express train car of the DRG with open scissor gate transitions, connected to each other. Available in N gauge for the first time.